As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to change the global transportation landscape, a seamless and intuitive charging experience is critical to encouraging more people to adopt EVs. Complex charging station access, navigating multiple charging networks, and inconsistent payment systems can be a deterrent for potential EV owners or frustrating for those who have already made the switch to EV mobility. The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is coming and it will revolutionize the EV charging ecosystem. OCPP is designed to simplify communication between EV charging stations and management systems, ensuring flexibility, interoperability, and efficiency for a robust and user-friendly charging network.
What is OCPP – Open Charge Point Protocol?
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is an application protocol for communication between electric vehicle (EV) charging stations (also known as EV charging points) and EV charging management systems (commonly referred to as CMS). Essentially, OCPP acts as a common “language” and channel that enables seamless communication between these two key players in the EV charging ecosystem.
OCPP was originally created in 2009 to standardize the interaction between EV chargers and management systems. Despite the existence of proprietary protocols, OCPP stands out as a completely open platform. This openness gives charging station users the flexibility to connect any network to any charging station, promoting innovation, competition, and accessibility in the EV charging industry.
Advantages of OCPP
1. Providing flexibility and security to charging station owners
OCPP ensures that charging station owners can change network operators as needed, thereby protecting their investment and preventing asset obsolescence. If a charging station manufacturer exits the market, owners can migrate to another OCPP-compliant network without losing functionality. This open choice encourages competition between manufacturers and network providers, which reduces costs, improves service, and promotes innovation. As a result, EV charging infrastructure has expanded rapidly, providing EV drivers with more charging options.
2. Allows universal communication between charging stations and network service providers to cost-effectively provide grid services (such as demand response).
The transition to a net-zero emissions scenario in 2050 will bring a surge in electricity demand, driven primarily by the electrification of transportation, home heating, and other industries. At the same time, the widespread deployment of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, whose generation varies with weather and time of day, has also put additional pressure on the grid. These dynamic changes pose challenges to grid stability and reliability, prompting utilities to seek innovative solutions such as demand response programs.
What is demand response?
Demand response involves balancing grid demand by encouraging users to shift their electricity use to off-peak hours when energy is more plentiful or demand is less.
This is typically achieved through price incentives or other financial rewards. Demand response, combined with smart grids and energy storage systems, plays a vital role in maintaining grid flexibility, mitigating the impact of variable renewable energy, and ensuring grid stability during high-load hours.
Role of OCPP in Demand Response
For demand response programs to be successful, seamless communication between chargers and utilities is essential. Chargers must be able to dynamically adjust or suspend their use of electricity based on grid demand. OCPP leverages established channels of interaction between chargers and management software to facilitate this communication.

Advantages of OCPP Demand Response
· Cost-effectiveness: By leveraging existing communication infrastructure, OCPP minimizes the additional costs associated with integrating chargers into demand response programs.
· Enhanced flexibility: OCPP-compliant chargers enable operators to effectively participate in grid management initiatives and ensure that electricity supply and demand are balanced.
· Future-proof infrastructure: Combined with OCPP, charging networks can adapt to the changing energy landscape and support broader grid modernization efforts.
By integrating demand response capabilities through OCPP, operators can not only contribute to grid stability, but also enhance the value of their charging networks in a sustainable energy ecosystem.
3. Increase EV adoption through unified access and simplified user experience
A seamless and intuitive charging experience is critical to encouraging more people to use electric vehicles (EVs). Complex charger access, navigation of multiple charging networks, and inconsistent payment systems can discourage potential EV owners or frustrate those who have already made the switch to EV mobility.
OCPP certification addresses these challenges by establishing a set of standardized protocols that enhance consistency and interoperability across charging networks. By ensuring that chargers meet these standards, OCPP can minimize barriers to entry and promote a unified user experience, making EV charging more convenient.

Some elements of the consistent user experience maintained by OCPP certification include:
1. How drivers start charging
2. How drivers pay for charging
3. Access to chargers from a variety of networks through a single app or payment profile
4. Standardized billing across different charging networks
The Bigger Picture: Supporting EV Adoption
By reducing friction points in the charging process, OCPP creates an ecosystem that makes driving more convenient. This not only improves the experience for existing EV owners, but also reassures potential buyers that owning an EV is both practical and convenient. A unified charging infrastructure builds trust and encourages wider EV adoption, which is critical to accelerating the transition to sustainable transportation.
Ultimately, OCPP-certified chargers play a key role in creating a cohesive and user-centric charging network, ensuring drivers feel confident and supported as they adopt EV technology.
How does OCPP work?
In the previous section, we learned that the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) provides a unified solution for the communication method between charging stations and any central system, regardless of the vendor.
OCPP is the communication medium between EV charging stations and EV charging management systems. The next section describes how OCPP helps these two different groups in the EV charging ecosystem communicate with each other, and what other functions it has in addition to communication.
1. Message Exchange
OCPP allows charging stations and management systems to exchange messages about the current status of the charging station.
For example, messages can include:
· Whether the charger is available, in use, or requires maintenance
· When the charging process starts or stops
· Current consumption or dwell time meter
· Charging station diagnostic information
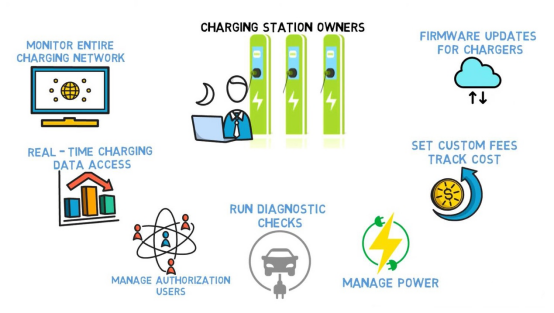
2. Remote Monitoring
Charging point operators can use OCPP to remotely monitor their charging stations.
3. Authorization
Charging point operators can use OCPP to authorize access to charging stations.
4. Firmware Update
The management system can send a firmware update request to the charging station, which can then confirm and perform the update.
5. Payment and Billing
Charging point operators can use OCPP to integrate different payment and billing systems.
6. Smart Charging
OCPP supports smart charging features such as load balancing and charging profile usage.
7. Demand Response Program
OCPP allows chargers to communicate with the grid or utility programs, which helps control electricity demand.
Introduction to existing OCPP versions on the market
In 2010, Open Charge Point Protocol 1.2 was released, and OCPP 1.5 was released in 2013. These early versions are no longer actively maintained by OCA, so we introduced subsequent versions, namely OCPP 1.6 released in 2015 and OCPP 2.0.1 released in 2020. OCPP 2.1 and OCPP 2.0.1 are backward compatible. OCPP 2.1 is expected to be released in the first quarter of 2025.

Two types of OCPP implementations
SOAP: Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) is a message-based protocol that uses XML to represent data. SOAP is a framework that allows messages to be sent between components on the Internet. The advantage of SOAP is that the standard covers the functions of sending and receiving messages. This makes rapid implementation possible.
JSON: JavaScript Object Notation is a lightweight data exchange format that is easy for humans to read and write, and easy for machines to parse and generate. It is easier to read and write than XML. It is based on a subset of JavaScript.
OCPP1.6
OCPP 1.6 builds on OCPP 1.5, incorporating years of practical experience and successful applications around the world. Since its launch in 2012, OCPP 1.5 has been widely implemented by suppliers and utilities around the world. On this basis, OCPP 1.6 introduces several major enhancements, including smart charging capabilities and support for JSON and SOAP over WebSocket.
This version also includes several improvements, such as clearer documentation and updates to enhance interoperability between different vendors’ products. Major new features include expanded diagnostic capabilities (such as reason codes), additional charging point status, and TriggerMessage capabilities, all of which are designed to better meet market needs.
OCPP 1.6 retains the core functionality of the previous version and introduces a number of updates and fixes for known obscure issues that make it incompatible with OCPP 1.5. These improvements are intended to provide better services to charging station operators (CPOs) and a better experience for electric vehicle drivers around the world.
Features of OCPP 1.6 include:
· OCPP 1.5
· SOAP and JSON versions
· Smart charging supports load balancing and the use of charging profiles
· (Local) list management support
· Additional states: Adds extra states to the charge point state enumeration to provide CPOs and end users with more information about the current state of the charge point
· Message sending requests, such as CP time or CP status
· Minor specification improvements (compared to OCPP 1.5)

OCPP 2.0.1
Compared to OCPP 1.6, OCPP 2.0.1 brings enhanced features and new capabilities. However, these improvements also make OCPP 2.0.1 incompatible with earlier versions (e.g. OCPP 1.6 and OCPP 1.5).
New Features OCPP 2.0.1 vs. OCPP 1.6
1. The Device Management (also known as Device Model) feature is used to get and set configurations and monitor charging stations.
Device Management (also known as Device Model) is a long-awaited feature, especially welcomed by CSOs who manage (complex) networks of charging stations (from different vendors).
It provides the following features:
• Inventory reporting
• Improved error and status reporting
• Improved configuration
• Customizable monitoring
All this helps CSOs reduce the costs of operating a charging station network.
Charging station manufacturers are free to decide how much detailed information about their charging stations to publish through
Device Management: for example, they can decide what can be monitored and what cannot be monitored.
2. Improvements to better handle large transactions
• One message covers all transaction-related functions
• Data reduction
OCPP 1.6 introduced JSON transport based on Websockets, which can significantly reduce mobile data traffic. OCPP 2.0 introduced WebSocket compression support, further reducing the amount of data.
3. Improvements in cybersecurity
The following improvements have been added to strengthen OCPP’s ability to resist cyber attacks:
• Security profiles (3 levels) for charging station and/or CSMS authentication and communication security
• Key management for client certificates
• Secure firmware updates
• Security event logs
4. Extended smart charging
In OCPP 2.0.1, the smart charging functionality has been extended (compared to OCPP 1.6) to support:
• Direct smart charging input from the energy management system (EMS) to the charging station
• Improved smart charging with local controllers
• Support for integrated smart charging of CSMS, charging stations and electric vehicles.
5. Support ISO 15118
Compared to IEC 61851, the ISO 15118 standard is a newer protocol for EVSE to EV communication. ISO 15118 allows many new features and safer communication between EVSE and EV. OCPP 2.0.1 supports the ISO 15118 standard, and the new features include:
• Plug and Charge
• Smart charging, including input from the electric vehicle
6. Improve customer experience
• More authorization options
• Display messages
• EV driver preferred language
• Tariffs and fees
7. Transport protocol: OCPP-J improvements
• Simple message routing
• No support for SOAP

Post time: May-21-2025
